In the current digital environment, having an online presence has become essential for both individuals and businesses. However, hosting a website can be a difficult task, particularly for people who are unfamiliar with web development.
Enter shared web hosting, a cost-effective and user-friendly solution that has gained immense popularity among website owners. This article explores shared web hosting in detail, providing an in-depth awareness of its benefits, drawbacks, and operational mechanisms.
What is Shared Web Hosting?
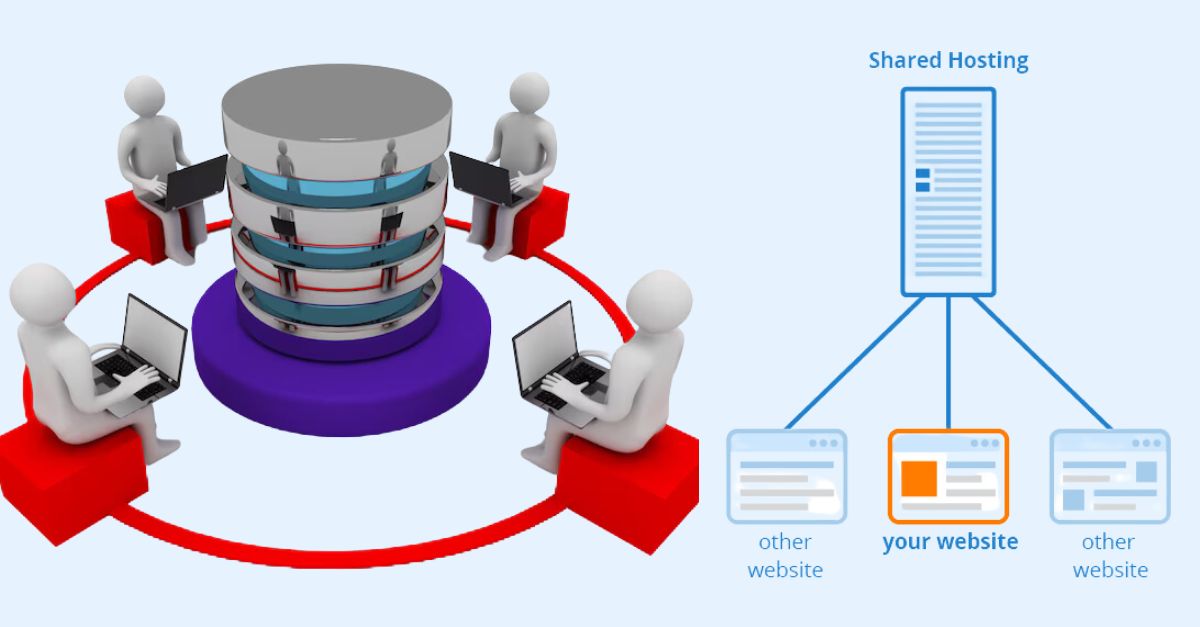
Shared web hosting is a type of hosting service where multiple websites reside on a single physical server, sharing resources such as disk space, bandwidth, and processing power.
This concept is similar to residing in an apartment complex (Server), where various tenants (websites) share common amenities and utilities (resources) while maintaining their individual living spaces.
How Does Shared Web Hosting Work?
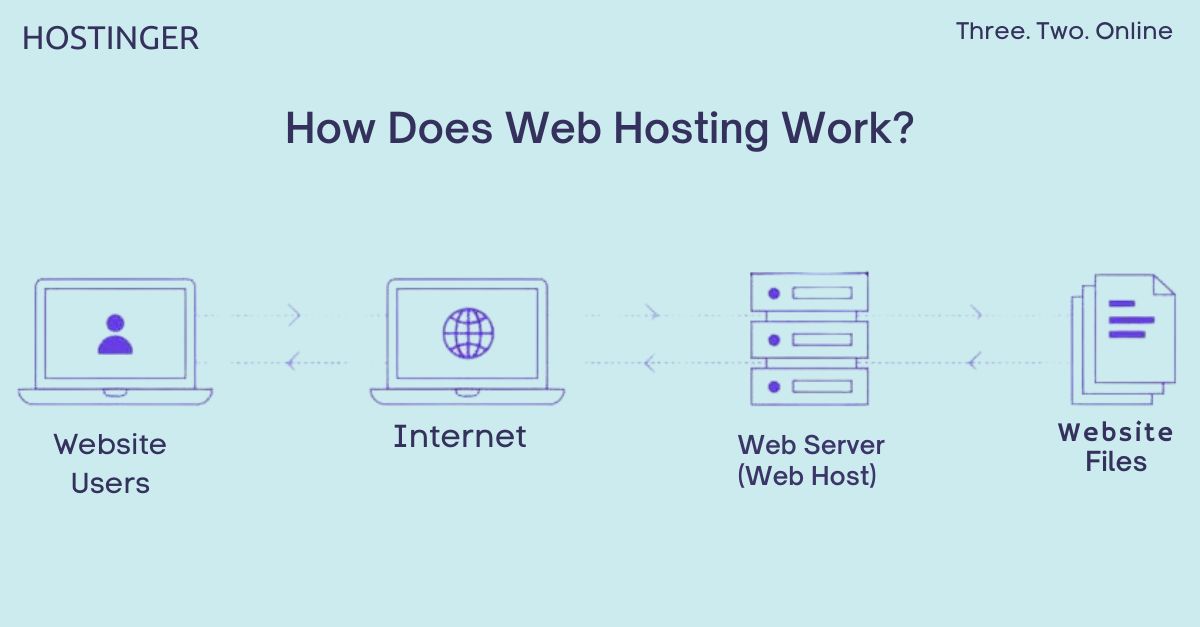
To better understand the mechanics of shared web hosting, let’s break it down into simple steps:
Server Setup: A hosting provider sets up a powerful physical server capable of handling multiple websites simultaneously.
Resource Allocation: The server’s resources, including disk space, RAM, CPU power, and bandwidth, are divided among the hosted websites, ensuring fair distribution.
Website Hosting: Each website owner is assigned a dedicated space on the server, known as a partition or account, where their website files, databases, and other necessary components are stored.
User Access: Website owners can access and manage their respective accounts through a user-friendly control panel (Cpanel), typically provided by the hosting provider.
Server Maintenance: The hosting company is responsible for maintaining the server, performing regular updates, implementing security measures, and ensuring optimal performance for all hosted websites.
It’s important to note that while resources are shared among multiple websites, each site remains isolated from the others, ensuring data privacy and security.
Advantages of Shared Web Hosting
Shared web hosting offers numerous benefits that have contributed to its widespread adoption:
1. Cost-Effectiveness
One of the main advantages of shared hosting is its affordability. Since the cost of maintaining and operating the server is distributed among numerous website owners.
The individual hosting fees becomes lower as compared to other hosting solutions, such as Virtual Private Server (VPS) or dedicated server hosting.
2. Ease of Use
Shared hosting is designed to be user-friendly, making it an ideal choice for individuals and small businesses without extensive technical expertise.
Most hosting providers offer control panels (CPanel), allowing users to manage their websites, databases, email accounts, and other essential features with ease.
3. Scalability
Shared hosting plans often offer scalability options as websites grow and require additional resources. Website owners can seamlessly upgrade to higher-tier plans.
These plans provide increased disk space, bandwidth, or additional features. This will save you time and you do not need website migrations or server configurations.
4. Reliable Support
Top shared hosting providers typically offer complete technical support, to their users. The trained professionals are available to address any issues or queries related to website hosting and management through live chat, email, or phone support.
5. Beginner-Friendly
Shared hosting is an ideal starting point for individuals and businesses. They offer a user-friendly environment that allows beginners to focus on building and maintaining their websites without the need for extensive technical knowledge.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Shared Hosting Provider
While shared web hosting offers numerous benefits, selecting the right provider is important to ensure ideal performance, security, and reliability for your website. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Uptime Guarantee

Uptime refers to the amount of time a website is accessible and functioning properly. Reputable shared hosting providers typically offer uptime guarantees, often ranging from 99% to 99.9%.
Higher uptime percentages indicate a more reliable service, minimizing the risk of website downtime and potential revenue loss.
2. Server Performance and Speed

The performance and speed of a shared server can significantly impact the loading times and overall user experience of your website.
Look for providers that prioritize server optimization, employ advanced caching techniques, and utilize solid-state drives (SSDs) for faster data access.
3. Security Measures

Website security should be a top priority when choosing a shared hosting provider. Evaluate the security measures implemented by the hosting company, such as firewalls, regular software updates, and SSL certificate support, to ensure the protection of your website and user data.
4. Bandwidth and Storage Limitations
While shared hosting plans offer limited resources, it’s essential to assess your website’s anticipated traffic and storage requirements.
Ensure that the hosting provider offers sufficient bandwidth and disk space to accommodate your current and future needs.
5. Customer Support
Reliable and responsive customer support is crucial, especially for those new to web hosting. Evaluate the hosting provider’s support channels, availability, and responsiveness to ensure that you can receive prompt assistance whenever needed.
6. Additional Features
Many shared hosting providers offer additional features to enhance functionality and convenience.
These may include free domain registration, website builders, content management system (CMS) installations (e.g., WordPress, Joomla, Drupal), email accounts, and database management tools.
Limitations of Shared Web Hosting
While shared web hosting offers numerous advantages, it’s essential to understand its limitations to make an informed decision:
1. Resource Sharing
Since multiple websites share the server’s resources, high-traffic or resource-intensive websites on the same server can potentially impact the performance of other sites.
This phenomenon is known as the “noisy neighbor” effect, where one website’s excessive resource consumption affects the overall server performance.
2. Limited Customization
Shared hosting environments often restrict users from making advanced server-level configurations or installing custom software. This limitation is in place to maintain server stability and prevent potential conflicts between websites hosted on the same server.
3. No Root Access
Root access, which grants the highest level of control over a server, is typically not available in shared hosting environments.
This restriction is implemented to ensure the security and integrity of the shared server and prevent unauthorized modifications that could compromise other hosted websites.
4. Shared IP Address
In a shared hosting environment, multiple websites share the same IP address. While this is generally not an issue for most websites, it can potentially cause problems if one of the sites on the shared server engages in activities that lead to IP address blacklisting or reputation issues.
When to Consider Upgrading to Alternative Hosting Solutions

As your website grows and your hosting requirements evolve, it may become necessary to consider upgrading to alternative hosting solutions that offer more resources and flexibility. Here are some scenarios where an upgrade might be beneficial:
1. High-traffic websites
If your website experiences a significant increase in traffic, shared hosting may no longer be sufficient to handle the increased load.
In such cases, upgrading to a Virtual Private Server (VPS) or dedicated server hosting solution can provide the necessary resources and performance to accommodate high-traffic volumes.
2. Resource-Intensive Applications
Websites that require resource-intensive applications, such as complex e-commerce platforms, video streaming services, or large databases, may outgrow the limitations of shared hosting.
VPS, or dedicated server hosting, can offer more computing power, memory, and storage to support these demanding applications.
3. Advanced Customization Needs
If your website requires advanced customizations, server-level configurations, or the installation of specialized software, shared hosting may not be suitable. VPS, or dedicated server hosting solutions, provide greater control and flexibility, allowing you to tailor the server environment to your specific needs.
2. Increased Security Requirements
For websites handling sensitive data or requiring heightened security measures, shared hosting may not offer the desired level of isolation and control.
VPS or dedicated server hosting, can provide dedicated resources and enhanced security features, ensuring the protection of your data and applications.
Conclusion
Shared web hosting has emerged as a popular and accessible solution for individuals and businesses seeking to establish an online presence.
Its affordability, ease of use, and scalability have made it an attractive option for beginners and those with limited technical expertise.
However, it’s crucial to carefully evaluate your website’s requirements, anticipated growth, and potential limitations to determine if shared hosting is the right choice for your needs.